Visible signs of iron in well water
It is not always possible to determine the presence of excess iron concentration in drinking water by external signs. The main criterion is smell and taste, but these factors appear in case of excessive concentration of the element. If the iron level is slightly exceeded (from 0.3 to 1 mg/l), the smell and taste of the water usually do not change significantly; the main signs of the presence of Fe are a ferrous taste and a cloudy rusty tint to the liquid. A water filter to remove iron from a well is a sure way to quickly and easily normalize the condition of water without the help of specialists.
There are several options for the presence of iron in water:
- Colloidal - does not produce sediment, but contributes to turbidity and yellowing of water
- Bacterial - is a product of the vital activity of bacteria, external manifestations are a gel-like coating on pipes and an iridescent film on the surface of the water
- Trivalent - does not dissolve in water, in a calm state of the liquid it settles to the bottom; when shaken, microparticles are evenly distributed throughout the entire volume, changing the color of the water
- Bivalent - difficult to determine by taste and color; laboratory analysis and special studies are required
Purifying water from a well from iron
The difficulty is that iron, being in a divalent state, dissolves in water, and obvious signs of increased content are not visually observed.
In this case, the metal can be seen in the form of a brown precipitate if the liquid is left to settle for several hours in a transparent container. If the contamination is associated with the activity of bacteria, then a film with multi-colored oil stains is formed.
Trivalent metal compounds are insoluble and are visible because the water turns brown and colored. In this case, settling is a more or less acceptable method of removing iron. This kind of problem occurs not only in houses where there is a well or well. The centralized system also serves as sources of pollution. Defending, although not the best method, is quite effective if there is no other way yet.
This is a way to get rid of metal impurities at home.
To do this, a storage tank is connected to the system, the volume of which is sufficient to provide a family with water for a day. It is impossible to say that the liquid will be completely purified. A precipitate will appear, and although the number of suspended particles in the solution will decrease, it is impossible to completely eliminate them in this way. To do this, you need to use other, more effective methods.
Aeration method of deferrization
This method of deferrization of water from a well is more effective.
It is necessary to ensure contact of the liquid with oxygen. In this case, the iron molecules are oxidized and react. To remove iron from well water using this method, the metal must be converted into a trivalent oxide compound, which becomes heavier and falls out as sediment at the bottom of the tank.
There are two technologies that allow you to achieve the desired effect:
- No pressure. Liquid is supplied to the tank and sprayed by nozzles. At the same time, it is enriched with oxygen from the air, which leads to the expected effect.
- Under pressure. A column-type scrubber is used, into which water is supplied under high pressure. To do this, a compressor is included in the system.
But there are other ways to purify water from iron from a well, which are based on the properties of this metal.
Ozonation process
It is assumed that an oxidizing agent will be used to act as a catalyst for the reaction.
Chlorine is not used now, since this element is not environmentally safe. The process is available on an industrial scale and cannot be implemented at home. It is necessary to install special equipment, and the use of chemical elements requires special permits.
Ion exchange method
Sodium ions are used as a cleaning agent.
When in contact with water, they cause a replacement reaction with iron ions. This is an effective way for a private house, cottage or even apartment. The filter takes up little space and can be installed in the kitchen in a cabinet under the sink. The system is autonomous and does not require constant monitoring. Filter maintenance is periodic in accordance with the regulations established by the manufacturer.
Reverse osmosis method
The technique is considered the best, since the filtered liquid is cleared of any impurities, including metal molecules. To do this, a complex is installed, which has several stages, the first of which is mechanical filtration of the liquid passed through the mesh. At the next stage, the water passes through the mineralizer. Here it is restored, and purification occurs at the molecular level. All necessary components of the treatment plant are available for free sale.
Application of reagents
This method is also applicable in production, as it requires specialized equipment.
The use of chemical compounds for absorption at home can lead to an uncontrolled reaction, which is dangerous to the life and health of people living in the house.
But there is still one way to trap iron molecules, and it is successfully used. Sodium hypochlorite is used as the active substance. As a result, molecules are formed that are insoluble in water and can be removed from the liquid mechanically. Special filters are used for this.
The dangers of excess iron in drinking water
The presence of high levels of iron in water is hazardous to health. In addition to the peculiar taste of ferrous water, over time you may begin to experience intestinal colic and stomach upsets due to the accumulation of iron in the liver and kidneys. Oxygen compounds of Fe contribute to the formation of dangerous carcinogens that cause cancer cells. They change the body's DNA and greatly increase the risk of cancer in biological systems.
Excess ferrous compounds in water are detrimental to the structure of tooth enamel; stones and cracks appear on it. Swimming in bad water often destroys the top layers of skin cells, causing dermatitis, allergic reactions and other skin ailments. In this case, the unprotected children's body especially suffers, so for families with children, a filter for purifying iron from water from a well will be an indispensable purchase.
In everyday life, deferrization will help prevent damage to pipes and dishes; plumbing fixtures and household items that regularly come into contact with water (washing machine, dishwasher, taps and water supply units) become unusable over time due to plaque and rust from bad water.
Where does the iron in water come from?
Possible reasons for increased iron concentration in water:
- If the soil contains deposits of sulfate ore or rocks of volcanic origin. In this case, even at a great depth of more than 50-60 m, water can contain more than 100 mg/l.
- If the soil is swampy. Swamp water may contain 1-5 ml/g of iron.
- If there is an industrial facility nearby: metallurgical, chemical, petrochemical, and it discharges wastewater into local water bodies. In this case, metals from the reservoir can be absorbed into the soil and enter underground sources.
- If the house has old rusty pipes (this is not relevant for wells, but for old high-rise buildings or for new buildings that are connected to the old water supply network).
- If the pH balance in the soil is disturbed.
Analysis of water for the presence of iron from a well
The simplest and most effective way to determine the degree of saturation of water with harmful impurities and organic compounds is to conduct laboratory tests. It is advisable to carry out such research before installing a filter to remove iron from water from a well ; this will help you choose an effective treatment system for your home or cottage.
Profwater offers its customers free laboratory water analysis quickly and efficiently. Research is carried out according to 6 main criteria - acid-base balance (PH), turbidity, hardness, PMO, mineralization and iron level.
Methods for deferrizing water
There are several ways to eliminate excess iron in water - chemically (using active compounds) or without the use of reagents. In each case, a special technique is chosen, taking into account the concentration of harmful impurities, the condition of the water supply and other factors.
Purifying water from a well from iron without the use of reagents
A modern filter for purifying water from iron from a well works in two ways - on the principle of aeration or through the use of multilayer filter compounds.
Aeration technology involves the creation of an artificial air exchange environment in which iron is converted into insoluble particles. The aeration system is made in the form of a sealed container, in which iron particles are oxidized under pressure or by ejection, after which hard, insoluble elements are retained in the filter layer.
A multilayer loading filter for water from a well from iron includes different-grained backfill layers with catalytic properties. The catalyst carries out a chemical reaction, due to which the iron crystallizes and settles at the bottom of the filter, from where it is subsequently washed out by the reverse water flow.
Purification of water from a well from iron with ion exchange resins
The use of ion exchange resins is considered one of the types of reagent water purification from impurities. Synthetic resin successfully removes ultra-high concentrations of iron, magnesium, calcium, manganese, radium (up to 15 mg/l) from water. It is made in the form of small balls that capture ions of various substances and impurities from water and absorb them. In exchange, previously dissolved ions are released into the water, and ion exchange occurs.
A system for purifying water from a well from iron, operating on the principle of ion exchange, is a universal method of deferrization and softening of drinking water. In this case, the water is purified from harmful impurities, and rust does not form in the container.
Methods for purifying water from iron
Since iron impurities in water are a common problem, a large number of effective cleaning methods have been developed against them. There are industrial cleaning methods and devices for apartments and private houses.
Reverse osmosis
The most effective method for removing iron-containing impurities. Can remove ferrous and trivalent iron.
The water flow passes through a fine-mesh membrane. The membrane holes are of such a size that only water molecules pass through. Iron impurities, due to their larger size, cannot pass through the pores and remain on the mesh, after which they are drained through the drainage (the mesh does not become clogged).
The disadvantage of the system is that the molecules of chlorine and some other chemical compounds are even smaller than water molecules. Therefore, reverse osmosis systems do not remove them, but let them through. To remove them, additional cleaning steps are required.
Ionic method
A filtration method that removes iron, manganese, and calcium. The filter uses an ion exchange resin that replaces iron with sodium and softens the water.
Disadvantages and features:
- the filter can only be used at metal concentrations up to 2 mg/l;
- the filter can be used if the water hardness is higher than normal;
- The filter can only be used for water that is free of organic matter.
Chemical method (oxidative)
The method is usually used only in industrial water treatment plants.
Chlorine, oxygen, ozone and potassium permanganate are used for cleaning. These oxidizing agents convert iron into ferric iron, which is then precipitated and removed.
For apartments and houses there is a simplified filtration system - catalytic. Magnesium dioxide is used as a neutralizer, which oxidizes iron-containing impurities and accelerates their precipitation.
Ferric iron removal
Most systems are designed to remove ferrous iron from liquids.
Ultrafiltration membranes with a cell size of 0.05 microns (microns) are used against trivalent impurities. The membrane traps impurities, which are then removed into the drain by backwashing.
Biological method of deferrization
Designed to remove iron bacteria. They are usually found in water at iron concentrations in the range of 10-30 mg/l, but can appear at lower levels.
To remove them, water is treated:
- chlorine or chelating agents;
- bactericidal rays.
Reagent-free cleaning
The principle is based on the interaction of MnO2 with iron: during the reaction, an insoluble compound is formed, which precipitates. For cleaning, filters with membranes containing manganese oxide are used. Membranes need to be cleaned periodically. The filters also have an auto-rinse function that flushes accumulated particles down the drain.
Ozone cleaning
A generator set is used for filtration. Inside it, the oxygen is cooled to +60º, dried, and supplied to the ozone generator. The resulting gas then passes through a stream of water, purifying it of iron and enriching it with oxygen.
Disadvantage of the method: such installations are expensive and are not beneficial for purifying large amounts of water (because ozone quickly decomposes).
Aeration
The method is based on the effect of oxygen. Pressurized air is supplied to the water tank from the well.
Oxygen oxidizes ferrous iron, releasing it into sediment, which is then washed into the drain.
Aeration systems are relevant for low iron concentrations (up to 10 mg/l).
Home cleaning without filters or installations
If you need to remove iron from a small amount of water (a bottle, for example), you can proceed according to this scheme:
- Let the water sit for at least 1 night. Impurities will settle to the bottom, after which the water will need to be filtered through a fine-mesh mesh.
- Boil the strained water.
- Freeze a container of boiled water.
After this, the water will get rid of most of the impurities and will become more suitable for drinking, even if it previously contained a high concentration of iron.
If additional cleaning is needed, activated carbon can be used. It needs to be wrapped in cotton wool and used as a filter: pass water through it.
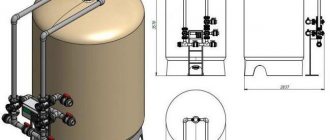
Popular types of filters for purifying water from iron from a well
The structure of the water purification system for removing iron from wells has several variations. There are reagent-free and reagent charging devices, as well as aeration filters - each of them is good in its own way, so before choosing the optimal device, you should study the advantages of a certain type.
- A reagent-free filter is a container with filter layers; it necessarily uses a catalyst to transform iron microparticles into a more sedentary form.
- Reagent filter - comprehensive purification of water from iron from a well is carried out in a similar way, but using an oxidizing agent or ion exchange resins.
- Aeration filter - works on the principle of aeration; oxygen is pumped into the cylinder through a compressor, causing iron to lose its ability to dissolve and its particles to be retained in the loading layers.
Homemade filter for deferrization of water from a well
A do-it-yourself filter for purifying water from iron for a summer residence does not have to be expensive.
By resorting to old-fashioned methods, it is possible to deferrize well water using improvised or inexpensive consumables. Ready-made store-bought filters are quite expensive. However, reagent systems for purifying well water can be made independently.
To make a filter you will need:
- Two horizontal tanks made of plastic and equipped with a large lid.
- A separate container intended for the active substance - bulk reagent.
- Fine sieve for collecting large solids.
- A set of plastic pipes, some of them equipped with taps.
The installation location of such a system depends on the frequency and intensity of use. If the water will be treated in winter, it is better to store the system in a heated room. The most suitable place is an attic, second floor or heated room.
Algorithm for assembling a filter for purifying well water:
- The base for the tank is installed. It is important that the base is reliable, strong and stable, since the weight of a container filled with water reaches several hundred kilograms.
- The containers are firmly fixed at the base. Connection to the water supply network. A special soldering iron is used to connect fittings and pipes.
- A container filled with a reagent and a sieve to collect solid impurities are loaded. The amount of reagent used depends on the degree of water contamination and the required volumes of purified water.
A homemade filtration system is not equipped with automation, so draining and cleaning is carried out independently.