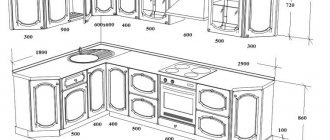
Why is it important to know the sheet dimensions before starting work?
Chipboards are almost always sold whole. Even if you need a small fragment of a slab, most often you have to buy the entire sheet. Sometimes in large industries involved in the sale and sawing of wood, you can only pay for the actual area of the cut sheet. The remains after cutting are used in production or are initially included in the price for the buyer.
Construction and repair work is a separate area - flooring and wall cladding. To calculate the size and required number of sheets, you will have to carefully measure the length and width (height) of the surfaces. By choosing the optimal dimensions and number of cuts, you can significantly simplify the work of laying the material.
Features of choice
The choice of chipboard is determined by its specific purpose . When making homemade furniture, priority remains with 1st grade material with a polished surface. Particular attention is paid to the emission class.
We recommend: Foam insulation for use in the construction of private houses. Composition, types and characteristics of polystyrene foam
In construction, you can safely use 2nd or even 3rd grade chipboard with an unpolished surface. Taking into account the application of protective coatings on it, you can pay less attention to surface quality and emission class.
For rooms with high humidity (kitchens, bathrooms, bathrooms, balconies), you need to choose moisture-resistant varieties. The slabs are selected taking into account the size of the room and furniture. We must try to avoid unnecessary waste, and the nomenclature allows us to choose the optimal dimensions of sheets.
What are the sizes of chipboard?
According to domestic regulatory documents, there are 18 and 9 gradations in the length and width of the slabs, respectively. The dimensions of the sheets vary from 1.83 to 5.68 m in length, and from 1.22 to 2.5 m in width.
The differences in sizes allow you to combine length and width combinations. Thanks to this, it is possible to select the optimal location of the cut fragments. Most often, you can buy slabs in three sizes on the market: 2.75 × 1.83 m, 2.62 × 1.83 m and 2.44 × 1.83 m. They are most convenient for transportation and universal when cutting.
Characteristics and dimensions
The technical characteristics of chipboard depend on the brand and type of product . They can vary within the following limits:
- sheet thickness – 10-40 mm;
- residual humidity – 5-9%;
- thermal conductivity coefficient – 0.08-0.26 W/(mhdeg);
- specific heat capacity – 1.65-1.85 kJ/(kg deg);
- water absorption – 11-87%;
- swelling (per day) in thickness – 4-28%;
- bending strength – more than 11-26MPa.
We recommend: How to choose wallpaper for your home - which is best for walls? Types and characteristics of material
Taking into account the structure and properties of the material, chipboard is classified into the following categories:
- By design: single-, three- and multi-layer sheets of particle boards.
- Brands according to basic technical characteristics (strength, moisture resistance, tendency to deformation) - P1 and P2 .
- The grade provides a division according to quality: first grade - polished surface with perfect smoothness, without visible defects; straight cuts; exact size match, main purpose – furniture manufacturing; the second grade is assigned when the first grade of chipboard is rejected according to some parameters; small chips on cuts and scratches on the surface are allowed; third grade - cheap chipboard of low quality with noticeable defects in the form of chips, cracks, and edge defects. It is used in construction for the construction of non-critical structures.
- According to the structure of the outer layer : fine-grained surface - it is well suited for lamination with polymer films; ordinary, standard sheets (medium grain) - when making furniture panels they are used for veneering; coarse-grained surface - such chipboards are more often used in construction.
- Surface treatment. According to the level of processing, polished and unpolished slabs are distinguished.
- The emission class is determined by the formaldehyde content , i.e. if possible, the release of this dangerous substance: class E1 - the content of free formaldehyde should not exceed 0.1 mg per 1 g of chipboard; in any circumstances, its release will not exceed the permissible limit, and therefore this material can be safely used in residential premises (even for children's furniture ); class E2 - content is limited to 0.3 mg for every 1 g of product. Use with caution.
- Water resistance . The following types of material are distinguished: standard plate with index A - deformation in water for 24 hours - 20-22%; standard chipboard with index B – deformation 30-33%; waterproof material - deformation does not exceed 16% (paraffin additives are used to increase moisture resistance).
- Fire resistance . Conventional chipboard is a combustible material. The fire-resistant version is made by introducing special additives - fire retardants . Domestic chipboards are not produced in a fire-resistant variety.
- Based on specific gravity , chipboards differ in low (no more than 540 kg/mm³), medium (540-760 kg/m³) and high (over 760 kg/mm³) densities.
We recommend: Mineral wool insulation - dimensions, which is better, characteristics. What and how to insulate using mineral wool
Chipboard sheets are available in different sizes, which allows you to choose a product based on your real needs. The thickness of the slabs starts from 1 mm and has a gradation of 1 mm up to 40 mm .
The thickness variation for sanded sheets does not exceed 0.3 mm, and for unsanded sheets it can be in the range of 0.4-1.6 mm (depending on the thickness). The minimum dimensions of the slabs are 1.2x1.8 m, and the maximum dimensions are not limited.
Moisture-resistant particle board
- dimensions: 2440x1830 (mm), 2500x1830 (mm), 2800x2070 (mm), 3060x1220 (mm);
- thickness: 12 (mm), 16 (mm), 18 (mm), 22 (mm), 26 (mm), 38 (mm);
- slabs must comply with moisture resistance classes P3, P4, P5.
Moisture-resistant chipboard is considered an ideal building material for leveling wall surfaces and working with roofing. The light weight and high density of the sheet (820 kg/m3) will provide an advantage when creating an insulating layer inside the roof.
note
Moisture-resistant boards, when exposed to moisture, swell by only 10% during the day.
Laminated particle board
- length: 2620 mm, 2800 mm;
- width: 1830 mm, 2070 mm;
- thickness: 8mm, 10mm, 12mm, 16mm, 18mm, 22mm, 25mm, 28mm.
Plates with a thickness of 8 mm to 18 mm are mainly used for the manufacture of furniture elements that will be subject to minimal loads ( wardrobes, MDF frame facades, sliding doors for wardrobes ).
Thicker slabs, from 22 mm to 28 mm, can withstand increased loads. They are more suitable for constructing kitchen tables or countertops .
Important!
The main disadvantage of laminated chipboard is considered to be insufficient moisture resistance and deformation in high-temperature environments.
Application of sheets of different thicknesses
To choose the right sheet of material, you need to know its optimal thickness. It affects the strength of the slab during transportation, as well as further use. The thicker the slab, the stronger it is, so it can be used in more loaded structures. The most popular sheet thicknesses are:
- 8-10 mm - most often used as a material for decorative partitions and unloaded furniture elements;
- 16-18 mm - common for laying floors (especially under linoleum and laminate), as well as for the production of most furniture products. The most wear-resistant floors can be obtained by using a heavier and thicker 20 mm slab;
- 22-25 mm - serve as the basis for thick doors, kitchen tables and loaded furniture structures;
- 28-38 mm - used to create especially durable tabletops and shelves that operate under heavy loads. Most bar counters are made from this thick chipboard.
What sheet properties depend on size?
The main parameter influenced by the thickness of the sheet is its strength and ability to resist external loads. As thickness increases, resistance to deformation increases, but flexibility decreases.
Thinner chipboard sheets have the ability to bend under mechanical stress. Thick canvases are much less elastic and are more likely to break than bend.
When purchasing a whole sheet of chipboard, do not forget to take into account the dimensions of corridors and staircase openings. Long sheets may not “fit” when turning or will break when trying to bend them.
Particle boards have high hardness, which also increases with increasing thickness. Impacts on heavy and thick slabs are likely to leave only small dents, while thin sheets may break through.
Calculation of the required amount of chipboard
To calculate the required amount of material, you can go in two ways - calculate the necessary layout of the cuts yourself or use special computer programs. In the first case, you will have to show perseverance and ingenuity, since finding the optimal layout of cutting lines will be quite difficult.
m 2
PC.
Required quantity: 0 pcs.
for area:
0 m2
.
Leave a request and we will offer you the best price for the material!
In the absence of good geometric imagination, models of the necessary parts can be cut out on paper, observing aspect ratios and a single scale. It is quite easy to combine cut out figures, alternating options for their relative arrangement.
Programs that help you decide on a cutting pattern are designed for interior design. The required number and shape of parts are entered into them, after which the optimal layout scheme on a canvas of specific dimensions is automatically calculated. A similar method is used in construction stores that cut materials to order from the client.
Comparison of prices of chipboard sheets of various sizes and manufacturers
The cheapest are slabs with a thickness of 10 mm. Blades 8, 12 mm and larger are more expensive. Let's consider the prices (rubles per sheet) of some common sizes of chipboard with the most popular thickness of 16 mm.
Table of dependence of chipboard sizes and prices per sheet (t. 16 mm) in rubles:
| Sheet size | Manufacturer | |||
| "Cherepovets FMK" | "Tomlesdrev" | "Altai-Forest" | ||
| 3500 × 1750 mm (6.1250 m2) | ||||
| 2750 × 1830 mm (5.0325 m2) | ||||
| 3030 × 1830 mm (5.5998 m2) | ||||
There are differences between the prices of chipboard from different manufacturers - the further the plant is located, the higher the cost will be after transportation to another region. Foreign manufacturers have even higher prices, but not always better quality. When planning your work, focus on commercially available materials - usually 4-6 options for sheet sizes are available, and the rest are delivered to order.
Before purchasing, look for a chipboard manufacturer in your area. Delivery of large quantities from the factory is much cheaper than from resellers.
Planning a chipboard cutting pattern is an important stage in construction and repair. The correct approach to sizing allows you to minimize material waste while reducing financial costs. Adequate selection of the thickness of the blades optimizes the weight and strength of the structure. The cost of the material increases with increasing dimensions and depends on the manufacturer.
The furniture industry has recently increasingly used another material instead of the usual wood - chipboards (chipboards), which have several varieties and are characterized by good performance.
The use of chipboard is not limited to the production of furniture; it has become widespread as a relatively lightweight and cheap material for universal use. What types of chipboard are there, standard sizes and areas of its use - this is what our article is about.
The chipboard production technology is quite simple: using a special adhesive composition, natural wood shavings are tightly connected to each other. Low-value softwood waste is used as the main “ingredient”, so such production is very justified from an environmental point of view.
Which furniture is better made from chipboard or MDF, you can find out in this
Often such designs are limited in width to two thin sheets of laminated film.
The thickness of the formed layer of the slab can be 8 - 38 mm. The most popular are chipboards with a width of 16-18 mm.
Advantages of DPS:
- Ease of processing.
- Low cost.
- Light weight.
- Good strength.
- Uniformity of structure.
- Large selection of chipboard colors.
All these indicators make the slabs very popular in various fields of construction.
Such plates also have disadvantages. They mainly concern the quality of the binders used. If the excess of formaldehyde resins is greater than the average, the use of such materials in residential premises is highly doubtful. To avoid harmful effects on the body, slabs should be selected according to their safety class, without using chipboards of inappropriate parameters.
The following types of chipboards are classified by surface type:
Recently, wood-based panels lined with special plastic coatings and polymer films have also appeared. This allows you to increase the moisture resistance of the material, but from a practical point of view, such slabs are very fragile. The quality of such chipboards will vary greatly depending on the manufacturer, so before purchasing it is advisable to check all hygiene certificates that allow the material to be used indoors.
What it looks like is indicated in the article.
Chipboard classification
We list the main types of classifications:
- Purpose
- Sheet sizes;
- Sheet thickness;
- Surface treatment;
- Chemical composition of the resin;
- Availability of special additives;
- Toxicity class;
- Grade (quality).
Let's look at these characteristics in more detail.
Purpose
- General purpose chipboard. There are no special requirements for such boards, such as water resistance or fire resistance. They are used mainly indoors and are used for the construction of partitions and the production of furniture, etc. Perhaps the main requirement is environmental friendliness, since indoors there is a restriction on the release of released harmful substances (formaldehyde) into the atmosphere. How basically these are chipboards using urea-formaldehyde resin.
- Chipboard for construction. Unlike general-purpose chipboards, these types of boards must have water resistance, fire safety, thermal insulation properties, water resistance, etc. As a rule, such boards are made on the basis of phenol-formaldehyde resins, less often on the basis of urea-formaldehyde resins, and appropriate additives are also used.
- Chipboard for special purposes. These products are produced to order and have chemical, physical properties, as well as dimensions determined by the customer.
Sheet sizes
The dimensions of chipboard sheets must comply with the current GOST. Manufacturers still adhere to this rule, however, there are cases when they deviate from it due to the fact that furniture production (or other large customers) dictate their wishes and requirements for the sheet form factor due to planning their production in order to minimize waste. Standard overall dimensions of sheets:
| Parameter | Size, mm |
| Length | from 1830 to 5680 |
| Width | from 1220 to 2500 |
We also provide a table with some typical (most common) sizes of chipboard sheets.
| Length, mm | Width, mm |
| 2750 | 1830 |
| 2620 | 1830 |
| 2440 | 1830 |
Sheet thickness
Chipboard is a fairly versatile material and has a wide range of applications. There are sheets with different thicknesses. As the thickness of the sheet increases, its strength increases, but its flexibility and ductility decreases. Thus, the thickness of the sheet largely determines the scope of its application.
| Thickness, mm | Purpose |
| from 8 to 10 mm | Decorative elements in furniture production and interior decoration |
| from 16 to 18 mm | Furniture production, as well as as a basis for laying floors (under linoleum and laminate) |
| from 22 to 25 mm | Doors, countertops, highly loaded furniture structures |
| from 28 to 38 mm | Production of highly loaded furniture and structural elements. For example, bar counters, massive countertops, etc. |
Surface treatment
When describing the production process of particle boards, the surface treatment process was mentioned, so three main types can be distinguished:
- Sanded plate. As the name implies, the surface of such slabs is ground using special grinding machines, resulting in a perfectly flat and smooth surface. Among themselves, craftsmen call such slabs white (or simply squirrels).
- Not sanded plate. Of course, the surface of the slab is processed and leveled, however, the process of fine grinding and finishing is not carried out and the quality of the surface is much inferior to ground samples.
- Laminated board. These are slabs whose surfaces are covered with special films that have the following purposes:
- Tinting. Films can have the required color or pattern.
- Protection. The plank is waterproof, therefore it protects the slab from exposure to moisture, which is destructive.
- Strength. The films are very durable and protect the surface of the slab from external mechanical influences.
Chemical composition of resin
The following types of resins can act as a binding element:
| Type of resin used | Advantages | Flaws | Application |
| Phenol-formaldehyde | Moisture resistanceLow cost | Increased harm to humans due to the release of harmful substances in the air | Outdoor construction structures |
| Melamine-formaldehyde | Moisture resistanceEnvironmentally friendly | High price | Special productions |
| Urea-formaldehyde | Low costLow moisture resistanceLow cost | Small release of harmful substances | More than 87% of all chipboards produced are made using this type of resin |
Availability of special additives
Special additives are often added to the resins to improve the physical and chemical properties of the chipboard sheet.
| Additive | Description |
| Fire retardant | This is an additive that improves the fire safety of chipboard. |
| Antiseptic | This is an additive that prevents the process of decay (formation of fungus, mold, etc.) |
| Paraffin emulsion | This is an additive that increases the moisture-resistant characteristics of the slab. The marking contains the letter “B”. |
Toxicity class (formaldehyde emissions)
Since not only different types of resins can be used in the production process (see “Chemical composition of resins”), but also within each type there are specific manufacturers of these resins, resins may differ in composition, additional classes of toxicity of harmful substances are introduced (presence of formaldehyde) .
| Toxicity class | Formaldehyde content | Harm level |
| E0 | Practically = 0 | Short |
| E1 | up to 10 mg per 100g dry slab | Average |
| E2 | from 10 to 30 mg per 100g dry slab | High |
Video about the dangers of using chipboard in residential premises.
Grade (quality)
The grade of chipboard is a basic characteristic indicating the quality of the board.
| Slab type | Description |
| 1 | The following are not allowed: · protrusions and depressions, · resin, paraffin and other stains; · chipped edges and chipping of corners. |
| 2 | The following are allowed: · chipped edges within deviations along the length (width) of the slab; · grinding defects (no more than 10% of the area); · to a greater extent (compared to the first grade) the presence of inclusions of bark and large fraction of chips. |
| Off-grade slab (OPN) | Will not satisfy the parameters of either the first or second grade |
Slab sizes
The production and dimensions of finished chipboards are regulated by state standards, so the dimensions of quality products will meet the following criteria below.
You can find out which ones exist by reading the article.
Main dimensions of chipboards:
- Thickness from 8 to 38 mm.
- Width from 800 to 2070 mm.
- Length from 1200 to 5680 mm.
Dimensions given may vary depending on manufacturers and purpose. The thicker the slab, the larger the dimensions it can withstand, but for domestic needs chipboards thicker than 16 mm and whose length exceeds three meters are rarely used. How much does it weigh? The weight of one sheet ranges from 40 to 70 kg, depending on the dimensions.
Basic parameters of particle boards
Despite the fact that at first glance all slabs of equal dimensions look approximately the same, in fact they differ in a number of parameters. The basic requirements for chipboard are contained in a special standard (GOST 10632-2007), according to which several different classes of these products are distinguished.
Chipboard varieties
Depending on the quality of surface treatment, three types of the material under discussion are distinguished:
- First grade. Complete absence of chips on the surface of the sheet, perfectly smooth edges, no swelling. Most often, first grade chipboard is used for further processing, in particular for lamination.
First grade chipboard sheets - Second grade . The sheet has minimal deviations: small chips, scratches, delaminations. Such slabs are used mainly in the production of furniture, flooring or cladding for finishing.
- Third grade . This is a rejection of high-quality material, which may have differences in thickness, large delaminations, low density and other defects. The standard does not indicate how many chips there must be to classify a sheet as third grade.
Estimated cost of chipboards
The price of the material will be influenced by several factors. First of all, this is the type and overall dimensions of the chipboard. The degree of moisture resistance and the presence of a laminated edge also determine the cost, as well as the type of raw materials used in production. For ease of calculations, manufacturers offer two price list formats: price per square meter and a whole sheet of chipboard.
Estimated cost of different types (chipboard sheet size 16 mm)
| No.: | Chipboard type: | Dimensions, mm: | Cost, $: | ||
| Width | Length | Per meter² | Per sheet: | ||
| 1. | Sanded board grade I: | 1750 | 3500 | 2,6 – 3,1. | 12,1 – 14,1. |
| 2. | 1830 | 2440 | 1,9 – 2,2. | 8,6 – 10,7. | |
| 3. | 1830 | 2750 | 1,6 – 2,7. | 9,0 – 12,0. | |
| 4. | 1830 | 3060 | 2,5 – 3,0. | 11,1 – 13,9. | |
| 5. | 1850 | 2500 | 2,2 – 2,3. | 10,0 – 10,7. | |
| 6. | 2070 | 2800 | 1,8 – 2,4. | 10,8 – 13,3. | |
| 7. | Laminated chipboard: | 1830 | 2440 | 2,9 – 3,3. | 12,9 – 14,7. |
| 8. | 1830 | 2750 | 3,9 – 4,15. | 20,4 – 21,6. | |
| 9. | 2070 | 2800 | 4,3 – 4,7. | 26,9 – 27,5. | |
As you can see, the cost of chipboard of various configurations is an order of magnitude lower than the prices of similar fiberboards, and even more so natural wood. It is this factor that makes chipboard the most popular option for replacing wood for finishing work.
Chipboards are an excellent option for an environmentally friendly analogue of wood.
There are enough varieties of chipboard to choose the right brand for any kind of rough finishing work, furniture making and other household and industrial needs.
The slabs are available in a wide range of shapes and colors; the most popular is the thickness of 16 mm, which makes it possible to produce furniture of good strength and high performance characteristics. When choosing chipboard for interior work, you should definitely pay attention to the markings and composition of the material.
laminated chipboard 16 mm 2500x1830
Chipboard 16 mm 2620x1830
Chipboard 16 mm 2750x1830
Chipboard 16 mm 2800x2070
Chipboard 16 mm 2800x2070
laminated chipboard 16 mm 3500x1750
Composition and manufacturing features
In terms of their appearance and properties, particle boards can be quite diverse, but basically, they are usually divided into several categories and classes according to the pressing method, the type of wood raw materials and binding components used, and the type of cladding.
Production stages:
- Obtaining wood chips.
- Preparation for further processing and sorting.
- Mixing shavings with adhesive composition.
- Creation of a shaving carpet.
- Hot pressing followed by cooling of the resulting slabs.
- Sanding of slabs, their cutting and packaging.
Any sizes of laminated chipboards 16 mm thick from reliable manufacturers
The production of modern cabinet and upholstered furniture is practically impossible without the use of laminated chipboard sheets. Furniture parts made from 16 mm laminated chipboard of various colors and shades look attractive and solid, withstand heavy loads, are resistant to most detergents, scratches and chips, and are easy to process. You can buy just such a 16 mm thick laminated chipboard in our store. We offer you material from serious manufacturers: IKEA, Kronospan, ShKDP, EGGER, Sveza.
What you need to know about chipboard
Before purchasing sheets of laminated chipboard or finished furniture parts made of laminated chipboard with a thickness of 16 mm, it is worth learning more about this material. This composition is made from wooden sawdust and shavings impregnated with formaldehyde resins. Laminated chipboard differs from chipboard in that it is covered with a paper-resin film. This film initially looks like ordinary paper, but after impregnation with melamine resin it acquires hardness and rigidity, as well as a characteristic shine, after which it is applied to chipboard and becomes inseparable.
Such a film can be applied to wood chip sheets in two ways: lamination and lamination. In appearance and in price, such sheets are practically the same. However, in the first case, the coating is forever inseparable from the base, and in the second, it can peel off and come off in the corners. For this reason, when purchasing, pay attention not only to the size of the 16 mm chipboard sheet, but also to the method of applying the top coating.
It is also worth checking with the seller the class to which the material belongs. Considering that the slab contains formaldehyde resins, which are extremely undesirable for humans to breathe, environmental standards in this case are of great importance. Remember: only 16 mm laminated chipboards of class E1 are allowed for use in residential premises. If the sheets belong to class E2, then they are used exclusively for exterior work and non-residential buildings. From us you can only buy slabs of class E1.
The weight of 16 mm chipboard may also indicate the quality of the material. If the sheet is excessively heavy, then perhaps mistakes were made when drying it, and light products can be too brittle and fragile due to the low density of sawdust in them. Slight weight variations are normal between products from different manufacturers due to different manufacturing techniques. For example, the optimal weight for EGGER 16 mm laminated chipboard with parameters 2800 × 2070 mm is 67.5 kg. If the size of the EGGER laminated chipboard is 16 mm smaller, then the weight is correspondingly smaller. Kronospan 16 mm laminated chipboard will weigh the same due to the company using similar production technology.
Laminated chipboard (LDSP) is today considered the main material for the production of office, school, kitchen and children's furniture. Leading manufacturers produce rectangular chipboards, but with different parameters of sheet thickness, length and width. This variety of slab formats allows the furniture maker to choose the right size for each product in order to minimize the amount of waste and trimmings. Well, if the furniture materials market is presented in which each manufacturer differs from each other, then it makes sense for us to understand this issue in detail.
Density and weight
One of the most important indicators used when assessing the quality of chipboard sheets is their density. And, if previously it was believed that the higher this indicator, the more durable and durable the material is, today it has been proven in practice that this is not entirely true.
In fact, the main role in ensuring the load-bearing capacity of chipboard is played by the condition of its surface, which is capable of holding fasteners, in contrast to its internal part, which has a looser structure.
This fact is confirmed by data on the density and thickness of boards manufactured by one of the leading manufacturers of particle boards, the Kronospan company:
| Plate thickness, mm | Sheet density, kg/m3 |
| 8 | 740 |
| 10 | 720 |
| 16 | 680 |
| 20 | 670 |
| 22 | 660 |
| 30 | 620 |
| 32 | 600 |
| 38 | 600 |
Having analyzed the information presented in the table, we can conclude that the density of the sheets in the thickest thickness of Kronospan chipboard is less than 700 kg/m3, but this in no way affects the quality of this material.
The weight of chipboard is proportional to its area and thickness and depends on the size of the sheet of material. For example, for a sheet with dimensions 2750 x 1830 mm and a thickness of 10 mm, it is 37 kg.
laminated chipboard from
The Swisspan brand produces a large number of wood-based panel formats, which are in demand among furniture manufacturers. The company produces the following sizes of laminated chipboards:
- 2440x1830 mm thickness 25 mm
- 2440x1830 mm thickness 22 mm
- 2440x1830 mm 18 mm thick
- 2440x1830 mm thickness 16 mm
- 2750x1830 mm thickness 16 mm
- 2750x1830 mm thickness 18 mm
- 2750x1830 mm, 10 mm thick.
Slabs with a thickness of 16mm and 18mm are used for the manufacture of dressing rooms and wardrobes. Thicker laminated chipboard sheets are perfect for the production of kitchen table tops and other furniture elements that bear increased loads.
Dimensions and thickness
Chipboard is produced in a size range regulated by GOST 10632-2007, according to which the permissible gradation of board parameters can be as follows:
- Length: 1830 – 5680 mm (includes 18 standard values).
- Width: 1220-2500 mm (includes 9 standard values).
- Thickness: 3 mm or more, in increments of 1.
At the same time, standard sheets of the following thickness are considered the most popular in the construction market:
| Sheet thickness, mm | Application area |
| 8 | Manufacturing of door panels, office partitions and some furniture elements |
| 16 | Internal partitions of wooden houses, office furniture, subfloors |
| 18 | Sliding wardrobes, cabinet furniture, also used as a base for laminate or linoleum |
| 20 | Construction of rough floors |
| 22 | Production of various types of furniture elements, including tabletops, frames and table tops, etc. |
| 25 | Elements of exhibition structures, tabletops, door panels and window sills |
| 32 | Furniture parts subject to heavy loads |
| 38 | Countertops for kitchens and bars |
Due to their visual appeal and ease of processing, particle boards are actively used in the furniture industry. For this purpose, grade 1 chipboards with decorative coatings made of veneer, paper-resin film, laminate or varnish are used. Laminated chipboards have the same dimensions and characteristics.